|
X-rays are part of the electromagnetic
spectrum, which includes radio waves, microwaves, and
visible light. They have an extremely short wavelength
or high frequency, thus giving them high energy. X-rays
can penetrate most materials except lead shielding. They
are used in medicine and industry to examine structural
problems. When they were discovered, the "X" stood for
"unknown," because they were so mysterious. The name has
been used ever since.
Questions you may have include :
Creating and detecting x-rays
When a high energy electron is
accelerated into a metal target, x-rays are given off as
a result of the collision. This is usually done in an
evacuated tube. It is caused when the high energy
electron knocks the electron from an inner orbit in an
atom. When the atom replaces that electron, it gives off
the x-ray.
X-rays were discovered accidentally by
Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895 when he was experimenting with
a gas-discharge tube (something like a neon light). He
noticed some fluorescent paper across the room start to
glow, apparently from some unknown radiation coming from
the tube. He called it X-radiation. The "X" stood for
unknown, because the radiation was so mysterious. The
name has been used ever since.
Soon it was found that x-rays would pass
through the soft tissues of the body and make images on
a photographic film. In the early 1900s, legislators
tried to outlaw x-rays because they were afraid
scientists would be able to use them to see through
people's clothes. They did not understand that although
x-rays would go through clothes, the only thing that
could be seen would be the person's skeleton.
Since the Sun has extremely high energy
electrons, it is a source of natural x-rays. Their
energy is greatly diminished by the time they get to the
Earth.
Note that the way your television tube
works is that electrons are shot to the screen, where a
fluorescence material glows when it is hit by the
electrons, creating the image on the TV screen. These
electrons have high enough in energy to create low level
x-rays at the screen.
In early televisions, it was not
advisable to sit real close to the TV screens. Today,
the x-rays are only measurable a few inches from the
screen.
A common way to detect x-rays is with
photographic film. Since x-rays are electromagnetic
waves just like visible light rays, they also will cause
photographic film to be exposed. Usually, a special film
that is more sensitive to the x-ray wavelengths is used.
People used to have problems of having
their film exposed when putting a camera through an
x-ray machine at airport luggage checks. Now airlines
claim the x-ray intensity is so low that it will not
affect camera film. But I would still use caution.
A new way to detect x-rays that some
doctors and dentists are using is with a digital
detector, similar to one used in your digital camera.
This allows them to see the image immediately, instead
of having to wait to have the film developed.
Unfortunately, the x-ray detectors are quite expensive,
so many are not using them yet. (My dentist said his
detector cost $9000. And that is why he has to charge me
so much!)
Characteristics of x-rays
X-rays are part of the electromagnetic
spectrum, which includes radio, microwaves, visible
light, and ultraviolet rays. They have the same general
characteristics as other waveforms, but x-rays also have
specific characteristics related to their wavelength.
Like every waveform, x-rays have
velocity, wavelength, frequency and amplitude.
Since x-rays are electromagnetic
radiation, their velocity in a vacuum is the same as
visible light: 186,000 miles/second or 300,000
kilometers/sec. Its velocity through transparent matter
is less, according to the index of refraction for that
material at that wavelength.
X-rays have a very short wavelength
compared to other electromagnetic waves.
Wavelength Comparison
| Radio |
Approx. 1.5 kilometer or 1 mile = 1.5 x
105cm |
| Visible Light |
1/1000 centimeter = 10-3cm
|
| X-rays |
1/1000000 centimeter = 10-6cm
|
Only gamma rays coming from atomic
explosions have a shorter wavelength than x-rays.
The frequency of x-rays is its velocity
divided by wavelength:
Frequency = Velocity / Wavelength
The amplitude of an x-ray is equivalent
to its intensity or brightness. Just like a bright
visible sunlight can cause a burn, so too can an intense
x-ray burn the skin.
The way the various types of
electromagnetic radiation interact with matter is
determined by their wavelength. Since x-rays have a very
short wavelength, they have different characteristics
than visible light. The most interesting characteristic
of x-rays is their ability to pass through many
materials. But the detection of x-rays is similar to
that of visible light.
They easily pass through soft body
tissues, but they are somewhat blocked by hard material
like bones.
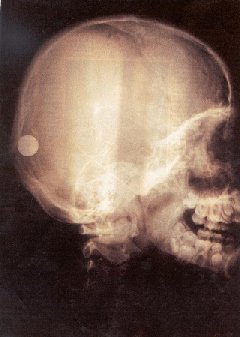
X-ray of a person's head
X-rays are almost completely stopped by
lead. That is why lead shielding is used to protect
people and things from excessive exposure to x-rays.
An important characteristic of x-rays is
that they will expose photographic film, even if it is
in a container. That is why you do not want to put a
camera with film through an airport x-ray machine.
Thus, if a beam of x-rays passes through
your body and exposes some film, a faint outline of your
soft tissues will be seen, but your bones will show up
distinctly. If a sheet of lead was put between the
source of the x-rays and the film, it would not be
exposed.
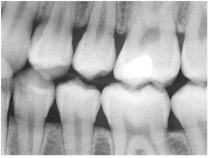
A dental x-ray requires holding a piece
of film behind the teeth
Medical and dental x-ray technicians
often wear a badge that contains photographic film to
monitor how much stray x-ray radiation they receive in
their jobs. The film in the badge is checked
periodically to see how much exposure was received.
X-rays can also be detected
electronically, with a detector similar to that used in
a digital camera to record visible light.
Uses of x-rays
There are a variety of uses of x-rays.
X-rays are being used in airports to
examine luggage for weapons or bombs. Note that the
metal detector that you walk through in the airport does
not x-ray you. It uses magnetic waves to detect metal
objects.
X-rays are also being used to examine
cargo luggage for illegal or dangerous material.
Another use of x-rays is in industry.
They can be used to detect structural problems and
cracks in metals that cannot be seen from the outside.
X-rays are used on commercial airplanes and bridges to
make sure there are no stress fractures or other
dangerous cracks in the material.
The most common use of x-rays is in
medicine and dentistry. X-rays are used to examine
inside the body to try to see if there is anything
abnormal. Broken bones, cancerous growths, and tooth
decay are some of the problems that can be detected by
an x-ray of a person.
Since x-rays have a very short
wavelength, they pack a lot more energy that radiation
with longer wavelengths. Although x-rays pass through
the body, they also can cause harm by altering atoms or
molecules they happen to hit.
If a person is exposed to high intensity
x-rays often or over a long period of time, there is the
potential of the person developing cancer in the exposed
area.
Medical and dental x-rays are very low
intensity, so the hazard is minimal. Still, x-ray
technicians go behind a lead shield when giving x-rays
because of the frequency of exposure. A person can
receive many medical or dental x-rays in a year with
very little risk of getting cancer from it. In fact,
exposure to natural radiation--such as cosmic rays from
space--pose a greater risk.
X-rays are electromagnetic waves with
extremely short wavelengths. They can pass though many
materials, but are stopped by lead. X-rays are used in
industry to examine metal for cracks and stress. They
are also used extensively in medicine and dentistry to
examine for broken bones and disease. Excessive exposure
to x-rays can harm a person's health, but most medical
practitioners are careful not to exceed suggested
limits. |