|
magnet is an object or material that
attracts certain metals, such as iron, nickel and
cobalt. It can also attract or repel another magnet. All
magnets have North-seeking (N) and South-seeking (S)
poles. When magnets are placed near each other, opposite
poles attract and like poles repel each other. Various
electrical devices make use of magnets.
Some questions you may have include:
Types of magnets
There are permanent magnets, temporary
magnets and electromagnets.
A permanent magnet is one that will hold
its magnetic properties over a long period of time.
Magnetite
Magnetite is a magnetic material found
in nature. It is a permanent magnet, but it is
relatively weak.
Alloys
Most permanent magnets we use are
manufactured and are a combination or alloy of iron,
nickel and cobalt. Rare-earth permanent magnets are a
special type of magnet that can have extreme strength.
A temporary magnet is one that will lose
its magnetism. For example, soft iron can be made into a
temporary magnet, but it will lose its magnetic power in
a short while.
By wrapping a wire around an iron or
steel core and running an electrical current through the
wire, you can magnetize the metal and make an
electromagnet. If the core is soft iron, the magnetism
will diminish as soon as the current is turned off. This
feature makes electromagnets good for picking up and
dropping objects. Typically DC electricity is used, but
AC current will also result in an electromagnet.
Properties of magnets
Magnets always have two poles, come in
various shapes, and attract or repel other magnets.
All magnets have a North-seeking pole
(N) and South-seeking pole (S). In a compass, the side
marked (N) will point toward the Earth's North magnetic
pole. Thus, it is called the "North-seeking pole." Also
note that the Earth's North magnetic pole is not the
same thing as the North Pole. They are actually several
hundred miles apart.
NOTE: To avoid confusion, you should try
to be exact in what you are describing, especially
concerning magnets.
The magnet can be made into various
shapes. The bar magnet is the most common configuration.

Bar magnet
Magnets also can be square, spherical,
shaped like a horseshoe, and even shaped like a donut.
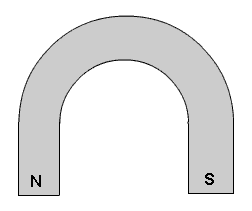
Horseshoe magnet
If you put an iron plate across the N
and S poles of a horseshoe magnet, that would
essentially "short circuit" the effect of the magnetism,
such that its strength would not be very great. As soon
as the plate was removed, the magnet would regain its
full strength. That method is sometimes used in magnets
that are temporary to help keep their magnetic
properties for a longer time.
An interesting characteristic of magnets
is that when you cut a magnet into parts, each part will
have both N and S poles.

Bar magnet cut into three parts
Magnets strongly attract iron, nickel
and cobalt, as well as combinations or alloys of these
metals.
Also, unlike poles of two magnets will
attract, but like poles will repel. Thus, N and S
attract, while S and S will repel each other.
Applications
There are numerous applications of
magnets.
You can magnetize a piece of steel by
rubbing a magnet in one direction along the steel. This
lines up the many of the domains or sections of aligned
atoms in the steel, such that it acts like a magnet. The
steel often won't remain magnetized for a very long
time, while the true magnet is "permanently" magnetized
and retains its strength for a long time.
If you use soft iron or steel, such as a
paper clip, it will lose its magnetism quickly. Also,
you can disorient the atoms in a magnetized needle by
heating it or by dropping the needle on a hard object.
The first true application of a magnet
was the compass, which not only helps in navigation by
pointing toward the North magnetic pole, but it is also
useful in detecting small magnetic fields. A compass is
simply a thin magnet or magnetized iron needle balanced
on a pivot. The needle will rotate to point toward the
opposite pole of a magnet. It can be very sensitive to
small magnetic fields.
Magnets are found in loudspeakers,
electrical motors and electrical generators.
A very common application of magnets is
to stick things to the refrigerator. Since the outer
shell of most refrigerators is made of steel, a magnet
will readily stick to it. The type of magnets used often
consists of a thin sheet of a magnetic material.
A magnet attracts iron, nickel, cobalt
and combinations of those metals. All magnets have
North-seeking (N) and South-seeking (S) poles. When
magnets are placed near each other, opposite poles
attract and similar poles repel each other. Magnets are
found in many of our electrical appliances. |