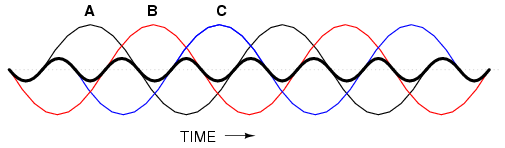
Harmonic phase sequences
In the last section, we saw how the 3rd
harmonic and all of its integer multiples (collectively
called triplen harmonics) generated by 120o
phase-shifted fundamental waveforms are actually in phase
with each other. In a 60 Hz three-phase power system, where
phases A, B, and C are 120o
apart, the third-harmonic multiples of those frequencies
(180 Hz) fall perfectly into phase with each other. This can
be thought of in graphical terms, and/or in mathematical
terms:

If we extend the mathematical table to
include higher odd-numbered harmonics, we will notice an
interesting pattern develop with regard to the rotation or
sequence of the harmonic frequencies:
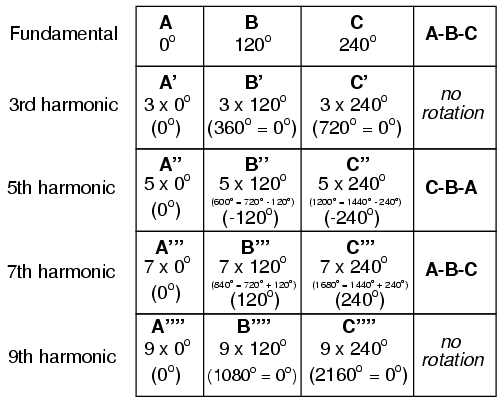
Harmonics such as the 7th, which "rotate"
with the same sequence as the fundamental, are called
positive sequence. Harmonics such as the 5th, which
"rotate" in the opposite sequence as the fundamental, are
called negative sequence. Triplen harmonics (3rd and
9th shown in this table) which don't "rotate" at all because
they're in phase with each other, are called zero
sequence.
This pattern of
positive-zero-negative-positive continues indefinitely for
all odd-numbered harmonics, lending itself to expression in
a table like this:
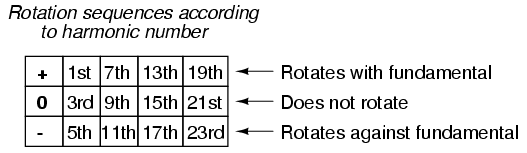
Sequence especially matters when we're
dealing with AC motors, since the mechanical rotation of the
rotor depends on the torque produced by the sequential
"rotation" of the applied 3-phase power. Positive-sequence
frequencies work to push the rotor in the proper direction,
whereas negative-sequence frequencies actually work
against the direction of the rotor's rotation.
Zero-sequence frequencies neither contribute to nor detract
from the rotor's torque. An excess of negative-sequence
harmonics (5th, 11th, 17th, and/or 23rd) in the power
supplied to a three-phase AC motor will result in a
degradation of performance and possible overheating. Since
the higher-order harmonics tend to be attenuated more by
system inductances and magnetic core losses, and generally
originate with less amplitude anyway, the primary harmonic
of concern is the 5th, which is 300 Hz in 60 Hz power
systems and 250 Hz in 50 Hz power systems.
|